In Costa Rica, a nation celebrated for its wealthy biodiversity and dedication to conservation, an alarming outbreak has lately shifted consideration from its picturesque landscapes to a burgeoning nationwide disaster. The New World screwworm, a flesh-eating fly larvae that targets the open wounds of mammals, has sparked a state of emergency, underscoring a extreme ecological and public well being problem. This pest, scientifically referred to as Cochliomyia hominivorax, has traditionally wreaked havoc throughout the Americas by preying on livestock, wildlife, pets, and even people, necessitating pressing and efficient management measures.
Almost seven months following the preliminary alerts, the state of affairs has escalated with the pest’s inhabitants on the rise, marking a major risk not solely to the agricultural sector but in addition to the general public’s well being. This improvement comes regardless of a long time of eradication efforts, together with these pioneered by the U.S. Division of Agriculture (USDA), which had beforehand seen success in North America. As Costa Rica confronts this renewed invasion, the main focus intensifies on methods to include and get rid of this invasive species, echoing the important significance of biosecurity and ecological administration within the area.
The Resurgence of the New World Screwworm in Costa Rica
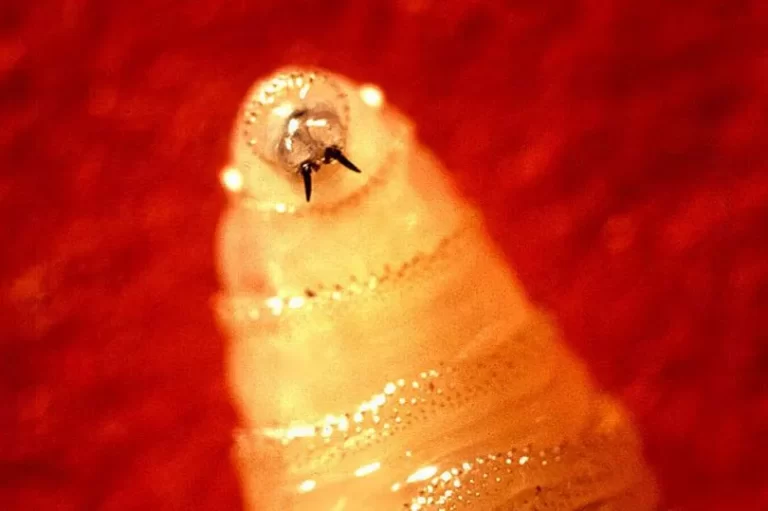
The New World screwworm (NWS) fly, a local parasite to the Americas, has re-emerged with troubling vigor in Costa Rica, posing a major risk to each home and wild animal populations. This resurgence is especially regarding given the screwworm’s desire for laying eggs within the open wounds of mammals, resulting in extreme infections that may be deadly if untreated. The fly’s lifecycle permits for fast inhabitants progress, with larvae that burrow into residing tissue, inflicting in depth injury. The preliminary detection of the NWS in Costa Rica was met with rapid concern, triggering reminiscences of previous outbreaks that had devastating results on livestock and wildlife, highlighting the important want for swift motion to forestall widespread injury.
Because the state of affairs progressed, the Costa Rican authorities, alongside worldwide well being organizations, has been monitoring the unfold intently. By March, the escalating state of affairs prompted the declaration of a nationwide emergency, the primary such response to a screwworm outbreak in a long time. This resolution was pushed by each the pace of the outbreak’s enlargement and its potential to disrupt not solely the agricultural sector but in addition the ecological steadiness, threatening species essential to the nation’s biodiversity.
The problem is compounded by the screwworm’s skill to unfold rapidly via animal populations, facilitated by the odor emitted from infested wounds, which attracts extra flies. This facet of the screwworm’s biology makes controlling the outbreak notably pressing, as every uncontrolled case can result in exponentially extra circumstances, placing an rising pressure on each pure and human assets. The nationwide emergency highlights the extreme influence of the screwworm on Costa Rica’s dedication to ecological and animal health, underlining the pressing want for efficient containment and eradication methods.
Lifecycle and the Perilous Influence of the New World Screwworm
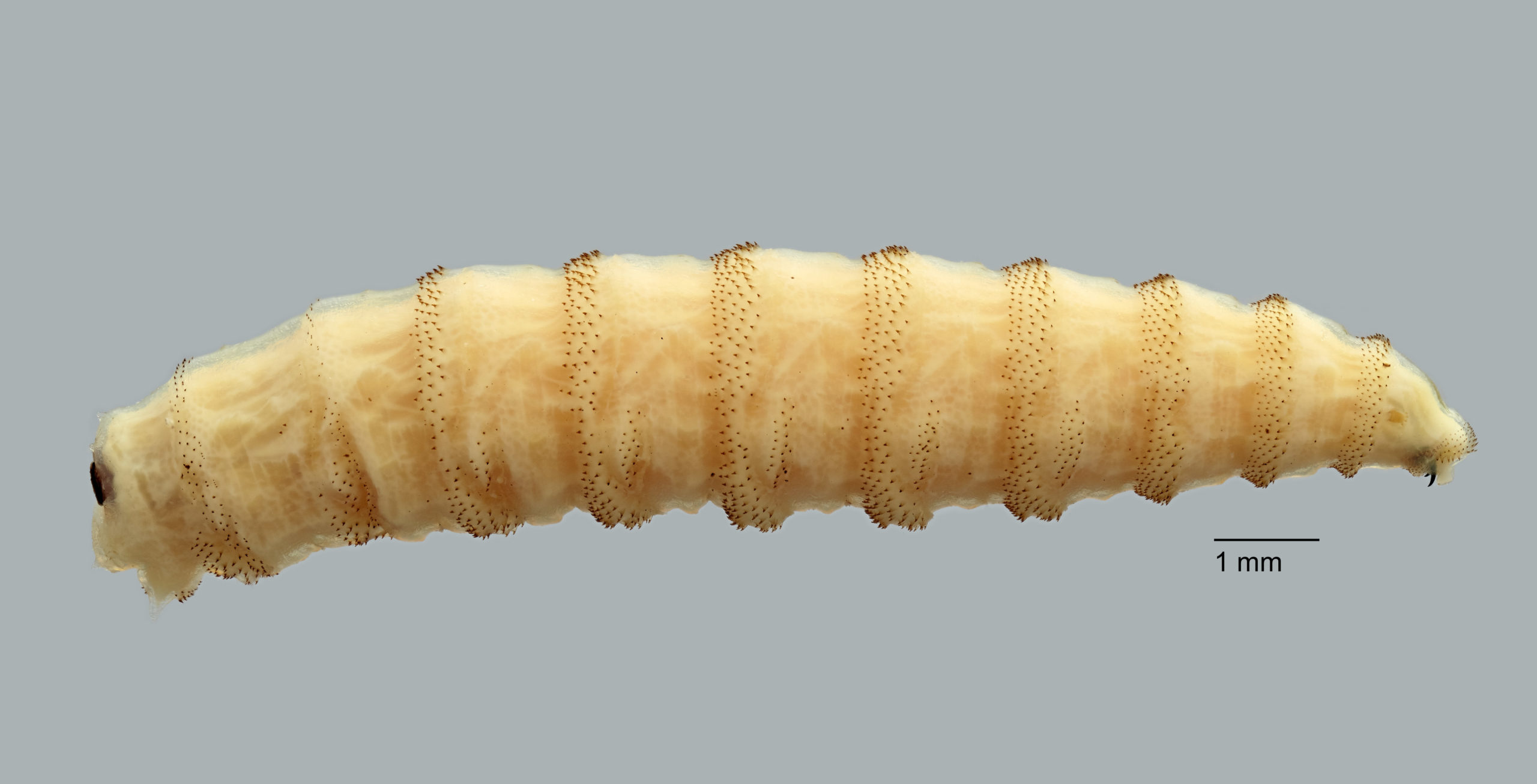
The New World screwworm (NWS) stands out amongst parasitic blowflies for its notably aggressive lifecycle and its desire for stay animal hosts. This fly has a chilling methodology of copy, laying its eggs particularly within the open wounds of mammals. The larvae, upon hatching, possess an alarming skill to burrow deep into residing flesh, consuming tissue as they develop. This exercise not solely causes extreme ache and potential dying to the affected animals but in addition poses important dangers to human well being, notably in rural or agricultural communities the place shut contact with animals is frequent.
The lifecycle of the NWS is very temperature-dependent, with hotter situations accelerating its development. In climates the place the typical temperature reaches round 29°C (84.2°F), the lifecycle from egg to grownup fly can full in as little as 18 days. This fast copy charge allows swift will increase in inhabitants underneath favorable situations, complicating efforts to manage outbreaks. In cooler climates, nevertheless, the event cycle extends, doubtlessly taking as much as three months. This variability performs a important position in shaping the methods used for managing and eradicating screwworm populations in several geographical areas.
The hazard of screwworm infestations extends past the preliminary bodily injury to animals. Contaminated wounds can appeal to different species of flies, resulting in secondary infections and complicating the restoration course of. The odor of an contaminated wound may also appeal to extra NWS females, making a vicious cycle of reinfestation that may devastate herds of livestock and wildlife populations. For new child animals, corresponding to calves and lambs, screwworm infestations will be notably deadly, usually focusing on the naval space and resulting in excessive mortality charges if not promptly handled. This facet of the screwworm’s influence highlights the important want for rapid and efficient intervention methods to guard animal welfare and stop broader ecological disruptions.

Eradication Efforts and Future Methods
The combat in opposition to the New World screwworm has traditionally seen revolutionary approaches, notably the sterile insect approach (SIT), which has been pivotal in controlling outbreaks. Developed by the USDA, this methodology entails breeding giant numbers of NWS flies, sterilizing the males via radiation, after which releasing them into affected areas. The approach depends on the truth that feminine NWS flies mate solely as soon as of their lifetime; therefore, mating with a sterile male successfully ends the reproductive cycle for that feminine, lowering future generations of the pest.
This strategy was first applied within the late Fifties in the US, primarily in response to screwworm outbreaks that severely impacted the livestock business. The strategy proved extremely efficient and was a key consider eradicating the pest from the U.S. by the Sixties. As a result of its success, related methods have been employed in different elements of the Americas, focusing on ongoing outbreaks and stopping the unfold of this invasive species. The eradication marketing campaign has not solely saved billions of {dollars} in livestock losses however has additionally contributed considerably to the welfare of the affected animal populations and their ecosystems.
Trying forward, Costa Rica’s latest declaration of a nationwide emergency highlights the necessity for continued vigilance and the appliance of confirmed eradication strategies like SIT. The federal government, in collaboration with worldwide our bodies such because the USDA and native well being businesses, is intensifying efforts to curb the unfold of the NWS. This contains rising surveillance, bettering fast response methods, and fascinating with communities to lift consciousness about prevention and early detection. The objective is to not solely management the present outbreak but in addition to ascertain a long-term technique to forestall future infestations, guaranteeing the security and well being of each animals and people in affected areas.

Lengthy-Time period Implications and Collaborative Efforts
The continued battle in opposition to the New World screwworm in Costa Rica not solely impacts the rapid well being of animal populations but in addition has broader implications for the nation’s financial system and public well being techniques.
The potential for screwworms to quickly infest giant teams of livestock and wildlife can result in important financial losses in agriculture and ecotourism, sectors very important to Costa Rica’s financial system. Furthermore, the risk extends to human well being, notably in rural communities the place shut interplay between people and animals is frequent. To deal with these challenges, a collaborative effort amongst varied stakeholders is essential. This contains:
- Authorities and coverage makers: Implementation of stringent insurance policies and assist for analysis into more practical management measures and coverings.
- Agricultural and wildlife administration communities: Adoption of finest practices in animal husbandry and wildlife care to attenuate the chance of screwworm infestations.
- Healthcare suppliers: Growing consciousness and coaching amongst healthcare professionals to acknowledge and deal with screwworm infections promptly.
Moreover, worldwide cooperation performs a pivotal position in screwworm administration, because the pest is aware of no borders. Sharing profitable eradication methods and steady monitoring can assist forestall the unfold of screwworms to new areas. This cooperation must be aimed toward not solely controlling the present outbreak but in addition at establishing sturdy preventive measures to protect in opposition to future re-emergences.
Finally, the combat in opposition to the New World screwworm is a take a look at of resilience and innovation. By leveraging each conventional strategies and technological developments in pest management, and fostering a tradition of vigilance and cooperation, Costa Rica can hope to regain management over this pest and stop future outbreaks, safeguarding each its agricultural heritage and pure biodiversity.
Complete Prevention and Management Suggestions
Managing and stopping outbreaks of the New World screwworm requires a multifaceted strategy that entails group consciousness, vigilant monitoring, and the strategic use of eradication methods. Listed here are some detailed ideas to assist stakeholders successfully fight this invasive species:
- Conduct frequent checks: Often examine all animals for wounds or indicators of an infection, notably in environments the place screwworms are recognized to be lively. Early detection is essential for efficient remedy and containment.
- Fast veterinary care: Any wounds discovered must be handled instantly by a veterinarian to forestall egg deposition by screwworm flies. Use acceptable wound dressings and medicines as beneficial by well being professionals.
- Protecting clothes for animals: Take into account using protecting gear corresponding to wound covers or fly-repellent clothes for animals in high-risk areas.
- Quarantine new or contaminated animals: Isolate any new or contaminated animals to forestall the unfold of infestation to wholesome populations.
- Sanitation: Keep excessive requirements of cleanliness in animal housing to cut back the attractiveness of those areas to screwworm flies.
- Consciousness applications: Conduct group outreach applications to coach farmers, pet house owners, and most of the people in regards to the dangers of screwworms and the significance of immediate remedy of wounds.
- Monitoring and surveillance: Make the most of traps and common surveys to observe screwworm populations and consider the effectiveness of ongoing management efforts.
These methods, when applied collectively, can considerably cut back the influence of New World screwworm outbreaks and safeguard the well being of livestock, wildlife, and doubtlessly human populations. Partaking the group and sustaining rigorous management measures are important for the profitable eradication and long-term administration of this devastating pest.

Remaining Ideas on Costa Rica’s Ecological Disaster
The resurgence of the New World screwworm in Costa Rica presents a formidable problem that calls for rapid and concerted motion. As this nation, famend for its dedication to environmental stewardship and biodiversity, faces this urgent disaster, the necessity for an built-in strategy turns into paramount. The battle in opposition to such a resilient pest underscores the broader implications for world ecological well being and the interconnections between human, animal, and environmental well-being.
Costa Rica’s response, combining rigorous surveillance, group engagement, and revolutionary eradication methods such because the sterile insect approach, highlights the important position of adaptability and worldwide cooperation in addressing biosecurity threats. The teachings realized right here lengthen past nationwide borders, providing worthwhile insights into the dynamics of pest management, the significance of early detection, and the effectiveness of proactive measures.
Because the world watches and helps Costa Rica’s efforts, this episode serves as a reminder of our shared vulnerability to ecological disruptions and the significance of sustaining vigilance in conservation practices. By fostering a tradition of knowledgeable consciousness and collaboration, we are able to hope to not solely overcome such challenges but in addition forestall their recurrence, guaranteeing the safety of our invaluable pure assets for future generations. This proactive stance is crucial not only for Costa Rica however for the worldwide group, emphasizing our collective accountability in safeguarding our planet’s biodiversity.