A brand new research describes a novel anti-cancer vaccine primarily based on antigen-producing micro organism that can tackle solid and metastatic cancers [1].
Invading an invader
Years in the past, scientists found that micro organism can colonize tumors [2]. Some micro organism are drawn to the tumor microenvironment attributable to components corresponding to necrotic tissue, hypoxia, and nutrient availability. For instance, Clostridium species desire anaerobic circumstances and have been explored in tumor-targeting therapies. Salmonella and E. coli strains have additionally proven an affinity for tumors [3].
This led to the thought of a microbial anti-cancer vaccine: utilizing tumor-targeting micro organism to enhance an organism’s immune response to most cancers. Nonetheless, this job has confirmed to be tough. In a brand new research revealed in Nature, researchers from Columbia College report creating a classy bacterial vector that’s efficient in opposition to strong tumors, that are thought of notably powerful targets.
Takes out most cancers, together with metastatic
It takes a number of mutations to show a wholesome cell right into a cancerous one. The merchandise of these mutations, which could embody full-length mutated proteins and truncated protein chains, can elicit an immune response (grow to be antigens).
The researchers recognized a number of such “neoantigens” in a sort of colorectal carcinoma and genetically engineered E. coli to provide them in giant portions. Mice have been then inoculated with most cancers cells. After tumors developed, the bacterial vaccine was injected instantly into the tumor microenvironment.
The micro organism readily colonized the tumors however not wholesome tissues. As anticipated, tumor antigens produced by the micro organism elicited a robust, multi-faceted immune response. A single injection successfully prevented tumor progress, with three out of seven mice exhibiting a whole response (full tumor eradication).
The researchers then difficult the duty: the mice have been inoculated with most cancers cells on each side of the physique, resulting in the looks of two tumors. Just one tumor was handled with the bacterial vaccine to see if this might produce a systemic response.
Because the researchers hoped, the remedy produced a sustained systemic immune response. The micro organism have been solely discovered within the handled tumors, however the untreated tumors additionally got here underneath assault by the immune system.
Injecting a drug instantly into the tumor will be difficult, so the researchers tried intravenous supply. They discovered that the micro organism have been rapidly cleared away from wholesome tissues however efficiently colonized the tumor and produced outcomes corresponding to intratumoral administration.
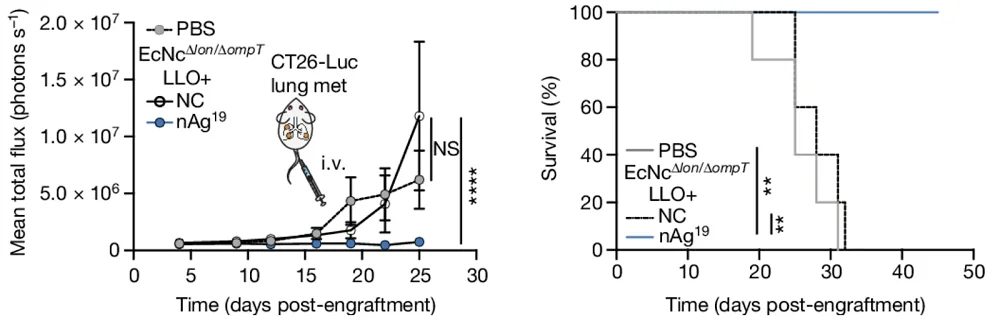
One other powerful take a look at was metastases. Metastatic (stage 4) cancers are just about incurable. On this research, lung metastases have been created by injecting carcinoma cells into the bloodstream. After the engraftment, the bacterial vaccine was additionally injected intravenously. Amazingly, all of the handled animals survived previous day 50 of the experiment, whereas all of the animals within the different teams succumbed to most cancers a lot earlier.
The researchers then tackled a extra aggressive tumor cell sort (B16F10 melanoma). In fact, they needed to engineer a brand new pressure of micro organism carrying melanoma-specific antigens. The remedy produced robust outcomes with localized tumors, blocking their progress nearly fully. With metastatic melanoma, the survival price was 60% within the remedy group versus zero within the management group.
A bespoke remedy
In keeping with the authors, their modified micro organism “recruit and activate dendritic cells, stimulate each neoantigen-specific and broad adaptive immunity, and scale back immunosuppression inside the tumor microenvironment.” The researchers additionally predict that their system may produce a synergistic impact when mixed with different remedies.
The brand new remedy must be tailor-made not solely to a selected sort of most cancers however to every affected person. “The time to remedy will first rely on how lengthy it takes to sequence the tumor,” stated Tal Danino, affiliate professor of biomedical engineering at Columbia’s College of Engineering and a number one writer on the research. “Then we simply have to make the bacterial strains, which will be fairly quick. Micro organism will be less complicated to fabricate than another vaccine platforms.”
Nonetheless, there’s an upside to that stage of personalization. Because the vaccine is predicated on a number of tumor-specific antigens, the most cancers will hardly have the ability to evade it by quickly mutating. “As a result of our platform permits us to ship so many various neoantigens, it theoretically turns into tough for tumor cells to lose all these targets directly and keep away from the immune response,” stated one other main writer, Nicholas Arpaia, affiliate professor of microbiology and immunology at Columbia College’s Vagelos School of Physicians and Surgeons.
Literature
[1] Redenti, A., Im, J., Redenti, B., Li, F., Rouanne, M., Sheng, Z., Solar, W., Gurbatri, C. R., Huang, S., Komaranchath, M., Jang, Y., Hahn, J., Ballister, E. R., Vincent, R. L., Vardoshivilli, A., Danino, T., & Arpaia, N. (2024). Probiotic neoantigen supply vectors for precision most cancers immunotherapy. Nature, 1-9.
[2] Yu, Y. A., Zhang, Q., & Szalay, A. A. (2008). Institution and characterization of circumstances required for tumor colonization by intravenously delivered micro organism. Biotechnology and bioengineering, 100(3), 567-578.
[3] Pawelek, J. M., Low, Okay. B., & Bermudes, D. (1997). Tumor-targeted Salmonella as a novel anticancer vector. Most cancers analysis, 57(20), 4537-4544.