A novel peptide might present a extra focused strategy to Alzheimer’s remedy by inhibiting two key Tau protein areas.
The seek for efficient Alzheimer’s illness remedies stays probably the most essential challenges in medical analysis in the present day. Regardless of billions in analysis funding and a long time of research, the progress towards discovering a definitive remedy has been restricted – present remedies provide solely modest symptomatic reduction or depend on early analysis, highlighting the necessity for extra revolutionary analysis avenues.
Longevity.Expertise: Alzheimer’s illness will not be solely a private tragedy for thousands and thousands of households but in addition a major public well being burden, projected to value trillions globally within the coming a long time as populations age [1]. To deal with this, researchers have more and more turned to tackling the underlying molecular mechanisms driving neurodegeneration.
One such mechanism is the aggregation of Tau proteins within the mind, which ends up in the formation of neurofibrillary tangles – a trademark of Alzheimer’s pathology. Tau proteins, essential for stabilizing neuron buildings, turn out to be poisonous once they clump collectively, forming tangles that disrupt mobile operate and result in cell loss of life. Researchers have recognized two essential “hotspots” on Tau proteins that encourage aggregation: one current in all Tau isoforms and one other discovered solely in these concerned in neurodegenerative illnesses like Alzheimer’s [2]. Most remedies goal solely one in every of these websites, limiting their effectiveness.
In a major development, a world staff, together with researchers from Lancaster College, the College of Southampton, Nottingham Trent College, Tokyo Metropolitan Institute of Medical Science and the College of Texas Southwestern Medical Centre, has developed a peptide-based drug, RI-AG03, which targets each of those Tau aggregation websites [3]. This dual-targeted strategy units RI-AG03 aside from different therapies that typically inhibit just one web site.
“Our analysis represents an essential step towards creating remedies that may forestall the development of illnesses like Alzheimer’s illness,” famous Dr Anthony Aggidis, lead creator of the research which has been printed in Alzheimer’s & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer’s Association. “By concentrating on each of the important thing areas on the Tau protein, this distinctive strategy might assist tackle the rising impression of dementia on society, offering a much-needed new choice for treating these devastating illnesses. [4]”
A novel mechanism of motion
RI-AG03 is a D-amino acid peptide; it’s retro-inverso in design, which isn’t a spell from Harry Potter, however means it’s extra steady and proof against enzymatic degradation – a major benefit for a possible therapeutic agent. Its peptide-based construction is designed to attenuate unintended interactions with different proteins, probably lowering negative effects which have hampered different remedies. RI-AG03 targets each the VQIVYK and VQIINK motifs on the Tau protein. The analysis staff discovered that the drug successfully inhibits the aggregation of a number of Tau isoforms, each in vitro and in animal fashions.
This dual-targeted inhibition is especially related, as Tau aggregation has been related to each kinds of binding websites. In testing, the staff found that RI-AG03 inhibits Tau aggregation via a mechanism that promotes the formation of enormous, amorphous aggregates as a substitute of extra poisonous, ordered fibrils. This diversion of Tau aggregation into much less poisonous buildings is assumed to mitigate the protein’s neurotoxic results. By way of this distinctive mode of motion, RI-AG03 additionally decreased cell loss of life in fashions that carefully simulate the consequences of Alzheimer’s illness [3].
Efficient in cell and animal fashions
The analysis staff examined RI-AG03 on fruit flies genetically modified to exhibit Tau-induced neurodegeneration. Not solely did the peptide cut back the buildup of Tau aggregates, nevertheless it additionally prolonged the lifespan of the flies – a formidable consequence given the sometimes quick lifespan of this species [3].
“Once we didn’t feed the flies with the peptide inhibitor, they’d a number of the pathogenic fibrils, which group collectively to make up a tangle,” defined Professor Amritpal Mudher, a contributing researcher. “However after we fed them with the drug, the pathogenic fibrils decreased considerably in amount. The upper the dosage given, the larger the development we noticed within the fruit fly’s lifespan [4].”
Related outcomes had been noticed in human cell line fashions, with RI-AG03 inhibiting Tau aggregation with out displaying toxicity at therapeutic concentrations [3].
Additional exams performed on biosensor cells on the College of Texas Southwestern Medical Middle confirmed RI-AG03’s efficacy; the peptide penetrated the cells and decreased the aggregation of Tau proteins, offering additional proof of its potential as a therapeutic intervention [3].
Nevertheless, Dr Richard Oakley, Affiliate Director of Analysis and Innovation on the Alzheimer’s Society UK, cautions that whereas these outcomes are promising, they symbolize an early stage of improvement.
“This analysis is taking promising steps in the direction of a brand new one-of-a-kind remedy which targets Tau, a harmful protein within the brains of individuals residing with Alzheimer’s, stopping it from clumping collectively,” he stated. “This drug has the potential to be extra focused than others at the moment being studied, and we hope it should lead to fewer poisonous negative effects.
“It’s essential to notice that the research is in its early levels, so we don’t but know if it should work or be protected for people, nevertheless it’s an thrilling improvement and we stay up for seeing the place it leads [4].”
Shifting ahead with RI-AG03
RI-AG03 is designed not solely to deal with Alzheimer’s but in addition to carry potential as a therapeutic agent for different tauopathies, as Tau aggregation is a shared function amongst neurodegenerative illnesses, together with frontotemporal dementia and progressive supranuclear palsy. Shifting ahead, the analysis staff plans to conduct additional preclinical research, together with trials on mammalian fashions, to guage RI-AG03’s efficacy and security comprehensively. Ought to these trials show profitable, the drug could in the end proceed to human scientific trials, bringing a novel dual-target strategy to the Alzheimer’s therapeutic panorama.
As Alzheimer’s illness continues to assert lives and pressure healthcare techniques worldwide, medicine like RI-AG03 may very well be a part of a shift in the direction of remedies that tackle the molecular roots of neurodegeneration. With additional analysis, RI-AG03 could provide sufferers not solely a respite from the signs of Alzheimer’s however an actual means to gradual or halt the development of this devastating illness.
As Richard Oakley neatly places it: “Analysis will beat dementia, however we have to make it a actuality sooner via extra funding, extra partnerships, and extra folks collaborating in dementia analysis [4].”
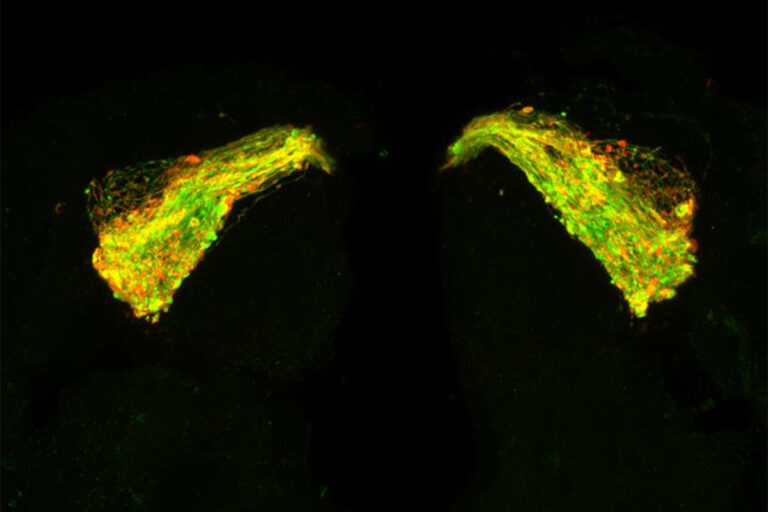
{Photograph} credit score: College of Southampton. Picture reveals the mind of a 7-day-old fruit fly with Tau expressed in a neuronal circuit utilized by the fly in olfactory reminiscence. The inexperienced outlines the neurons, that are beginning to swell and degenerate because of the Tau protein. The purple reveals the place Tau is increase in clusters alongside the neurons, beginning to kind the clumps that ultimately turn out to be rope-like fibrils.
[1] https://www.who.int/news/item/02-09-2021-world-failing-to-address-dementia-challenge
[2] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29988016/
[3] https://alz-journals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/alz.14246
[4] https://www.lancaster.ac.uk/news/promising-first-in-alzheimers-drug-development