In Cell, a staff of researchers, together with the founders of the biotech firm HepaRegeniX, has revealed a paper on HRX215, a molecule that encourages liver regeneration.
When the liver doesn’t regenerate
The researchers observe that the liver has a “almost limitless regenerative potential” below wholesome circumstances. Nevertheless, when its microenvironment modifications resulting from injury, this potential can grow to be misplaced [1]. This staff has revealed earlier work displaying that MKK4, which is a part of the MAPK stress response community, is a elementary regulator of this capacity and that inhibiting MKK4 encourages regeneration in liver cells [2]. No earlier small molecules to inhibit MKK4 have been revealed, and this staff claims to be the primary.
Liver progress with out tumors
A genetically engineered mouse mannequin, which has its MKK4 manufacturing suppressed within the presence of doxycycline, was used as the premise for the preliminary experiments earlier than the possible drug had been produced. 72 hours after the mice’s MKK4 genes had been silenced, these mice and mice in a management group had sections of their livers eliminated, and the mice had been examined 48 hours later. The variety of proliferating liver cells was significantly higher within the MKK4-silenced mice in comparison with the management group.
To check long-term security, the researchers silenced MKK4 in mouse populations for 12 months. There was no proof of toxicity, and lifespan was not considerably affected. The researchers maintain that as a result of MKK4 is a part of a stress response, silencing MKK4 will make no distinction within the absence of that response.
They carried out a security take a look at through the use of a mouse mannequin that’s exceptionally liable to liver tumors, after which fed these mice a eating regimen identified to induce liver toxicity [3]. They then injected these mice with liver cells from both the management group or the MKK4-silenced group. There have been no important variations between the teams, though the variety of liver tumors gave the impression to be decrease within the animals that had obtained the MKK4-silenced cells.
Drug discovery and mouse outcomes
Inspired by these outcomes, the researchers then started to conduct drug discovery. They analyzed the molecular construction of MKK4 and found that an current drug that has already been clinically permitted, vemurafenib, binds to it as an off-target impact. They modified this molecule, HRX215, to extra strongly give attention to MKK4, ensuring that it doesn’t have an effect on associated compounds which might be core parts of liver regeneration.
They then injected HRX215 into wild-type mice, evaluating them to a management group. Equally to the MKK4-silenced mice, these animals had no important bodily variations within the absence of liver injury. Dosing the animals with HRX215 earlier than exposing them to carbon tetrachloride, a molecule that induces liver injury, inspired proliferation of those cells and considerably decreased the quantity that had died. The protecting results had been the identical no matter whether or not the mice obtained the drug at .4 mg/kg or 10 mg/kg, suggesting {that a} low dose is ample.
Giving the mice HRX215 over an extended time period confirmed no opposed uncomfortable side effects. There have been no important variations in safety-related biomarkers. As an alternative, it gave the impression to be protecting in fashions of alcoholism and fibrosis, encouraging wholesome progress whereas discouraging cancerous tumors. That mixture is uncommon in drug results, and the researchers observe that some pathways which might be upregulated when MKK4 is inhibited in wholesome cells are downregulated as a substitute in most cancers cells.
From pigs to folks
When pigs have 80% of their livers eliminated (resection), they usually survive. Nevertheless, eradicating 85% of the organ normally results in acute liver failure and demise. Utilizing a complete of eight animals, the researchers examined their drug in opposition to 80% resection first, injecting them with it beginning a full day earlier than the surgical procedure. 43 hours afterwards, the management group had regenerated 160 milliliters of liver quantity, however the remedy group regenerated over 250 milliliters.
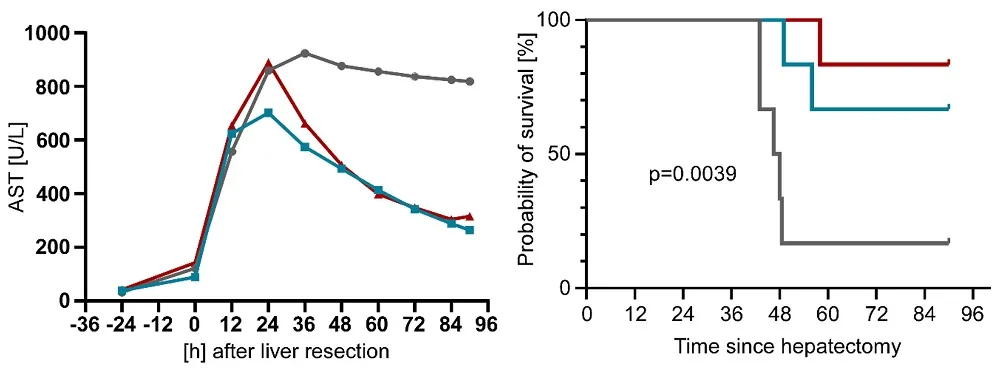
The researchers used a complete of 18 animals to testing 85% liver resection: six got HRX215 12 hours earlier than surgical procedure, six got the drug 12 hours after surgical procedure, and 6 had been in a management group. Bilirubin and ammonia rose within the management group way more within the management group than in both of the remedy teams, which carried out equally. Intracranial strain (ICP) rose within the management group however not within the remedy teams. AST, a marker of extreme liver injury, spiked in all three teams however quickly went down within the remedy teams. A lot of the handled animals survived, however solely one of many management group did.
These extremely encouraging outcomes led the researchers to carry out a Section 1 security trial in human beings. These trials are usually not powered to check the drug’s efficacy; reasonably, they’re meant to find out whether or not or not they result in opposed uncomfortable side effects. Thankfully, there have been no critical or extreme uncomfortable side effects, and transient, delicate uncomfortable side effects had been related between the placebo teams and the remedy teams. There have been additionally no important variations in blood cell counts.
The researchers maintain that their outcomes favor the event of a Section 2 efficacy research, which might decide whether or not or not the drug really helps regenerate the livers of human beings. If profitable, such a drug might probably assist the lives of a terrific many individuals affected by age-related or toxicity-related liver injury.
Literature
[1] Campana, L., Esser, H., Huch, M., & Forbes, S. (2021). Liver regeneration and irritation: from elementary science to medical purposes. Nature opinions Molecular cell biology, 22(9), 608-624.
[2] Wuestefeld, T., Pesic, M., Rudalska, R., Dauch, D., Longerich, T., Kang, T. W., … & Zender, L. (2013). A Direct in vivo RNAi display screen identifies MKK4 as a key regulator of liver regeneration. Cell, 153(2), 389-401.
[3] Wolf, M. J., Adili, A., Piotrowitz, Okay., Abdullah, Z., Boege, Y., Stemmer, Okay., … & Heikenwalder, M. (2014). Metabolic activation of intrahepatic CD8+ T cells and NKT cells causes nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and liver most cancers through cross-talk with hepatocytes. Most cancers cell, 26(4), 549-564.